Introduction
PVE is a hypervisor that allows you to run Virtual Machines using Linux technologies. It is built on Debian and is entirely open-source. It operates through a web-based GUI where you can manage your VMs, LXC containers, networking, storage, and more
Tips after installation:
Remove pop-up “no valid subscription”
run this command and clean cache of your broweser
sed -i.backup -z "s/res === null || res === undefined || \!res || res\n\t\t\t.data.status.toLowerCase() \!== 'active'/false/g" /usr/share/javascript/proxmox-widget-toolkit/proxmoxlib.js && systemctl restart pveproxy.service
This message will disappear if you run the above command or if purchase a subscription (enterprise env).
Fix Repositories for proxmox
in the web-gui navigate to your host –> update –> repositories and remove the enterprise one and activate the pve-no-subscription:
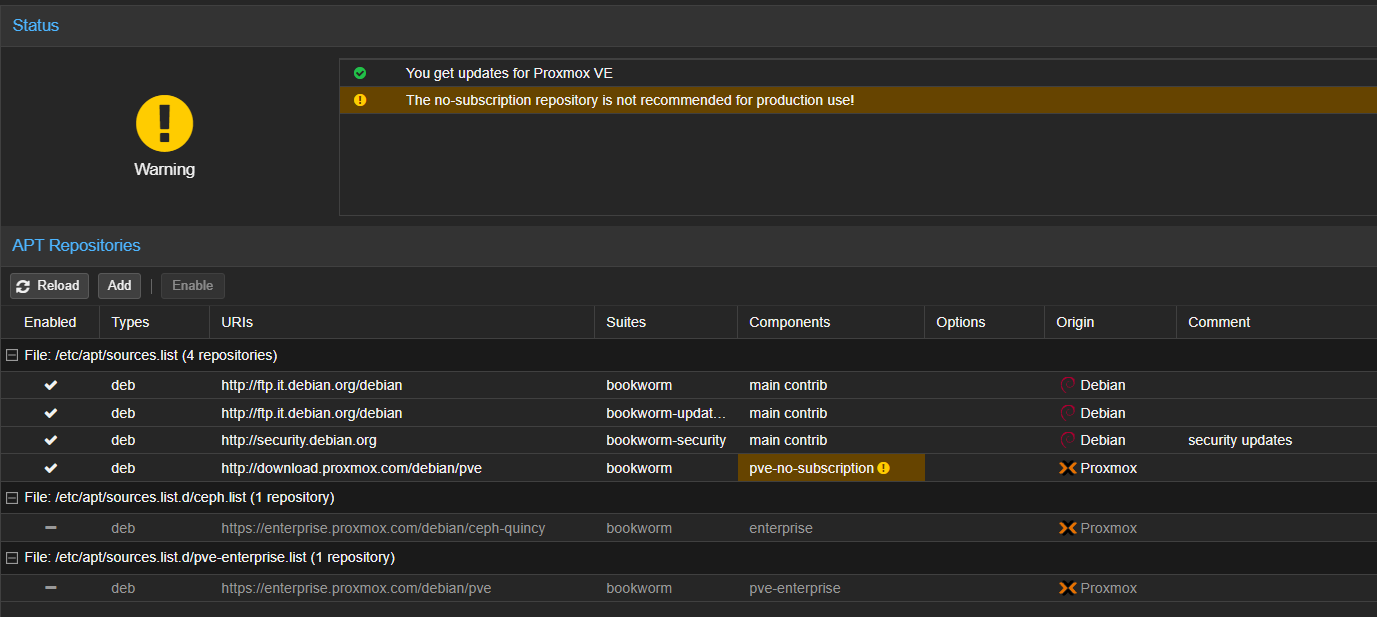
If you plan to use proxmox in a production environment I would suggest to take a better look online before changing the repositories
VMs vs LXC
What shoud I use?
VM: Virtual Machine provide a robust layer of isolation from the host system through virtual emulation of hardware components. This higher level of isolation ensures that if a VM encounters any issues or malfunctions, it does not affect the underlying host system or proxmox in this case.
LXC: Linux Containers, consume less resources compared to vms because they share the host system’s kernel. For example, you cannot create a Windows container on a Linux kernel, as Windows cannot run on a Linux kernel. This sharing of the kernel also means that they are inherently less secure than virtual machines, as any compromise in one container can potentially affect others on the same host
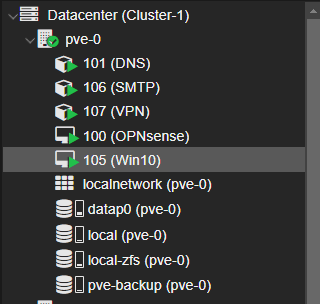
As you can see, I use LXC for straightforward applications like DNS, VPN, and email due to their lightweight nature. Meanwhile, for the Windows10 and the router machine, I utilize VMs.
Backup
I suggest to do backup of your vms/lxc on proxmox as it is very simple and straightforward and it’s the best practice for data-recovery
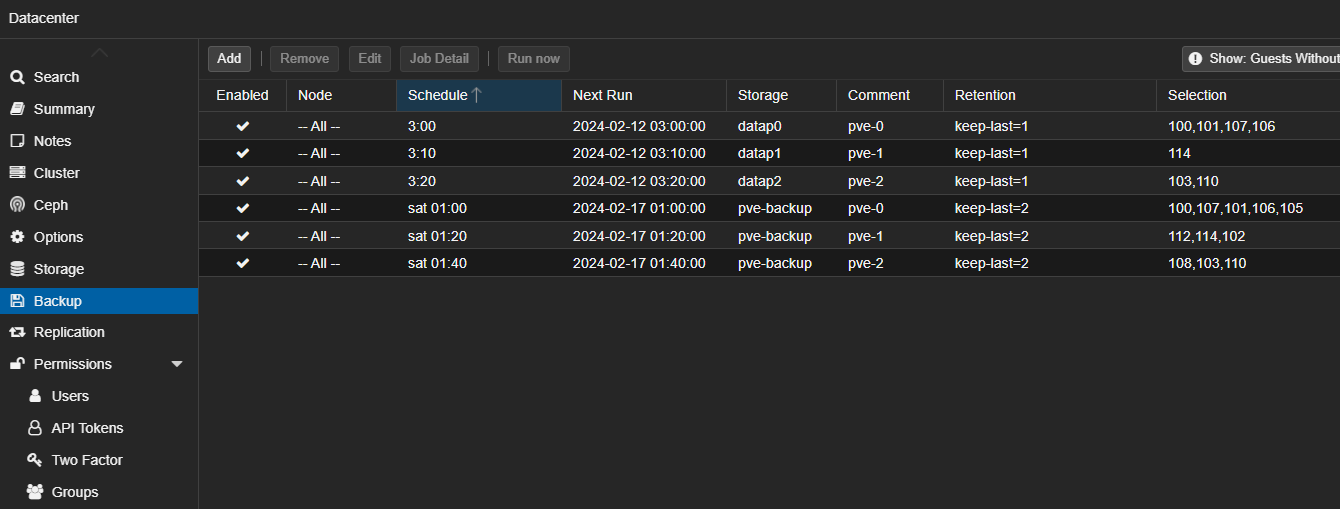
Backup option:
Connect nas to proxmox via SMB or NFS (datacenter->storage->add->SMB~NFS)
Use PBS and mount the backup storage (datacenter->storage->add->proxmox-backup-server)
Do manual backup of your vms on an external disk.
As you have connect an external storage you can do manual backup or schedule it in datacenter->backup (see image above)
I suggest to do backups outside of proxmox, so even in case it fails for whatever reason, you can just restore the backups in another pve machine and be up and running again.
About PBS you can install it in a VM inside proxmox but you shoud consider the point above.
An easy way to deploy services
I use this website to quickly and easily deploy a variety of services like media-server, operating systems, Docker, and more.
